Test Coverage
The Test Coverage Analyzer uses coverage report files generated from tests to perform analysis.
Enabling this Analyzer will show you coverage metrics like Line Coverage, Branch Coverage, Condition Coverage, and Composite Coverage. The Analyzer also looks at lines of code never executed by any tests and raises actionable issues for them.
This section covers steps to get started with the test-coverage Analyzer. Please first read the general configuration guide.
Configuration - .deepsource.toml
To enable the Test coverage Analyzer, ensure it is enabled in your .deepsource.toml configuration file. This can be done by adding the following entry:
[[analyzers]]
name = "test-coverage"
enabled = true
Setup Test Coverage
The analysis begins as soon as the Analyzer receives a valid coverage report. To do this, you can hook up the DeepSource CLI with your test CI and send the coverage report as soon as the tests finish.
Set up DEEPSOURCE_DSN environment variable
DSN is used to associate the coverage artifact with the repository. This needs to be configured before sending a coverage artifact for analysis.
To look up the DSN:
- Go to the Settings page of the repository dashboard in DeepSource
- Go to the Reporting Section
- You can either click on the click to copy button to copy your DSN or click on Reveal to take a look at it.
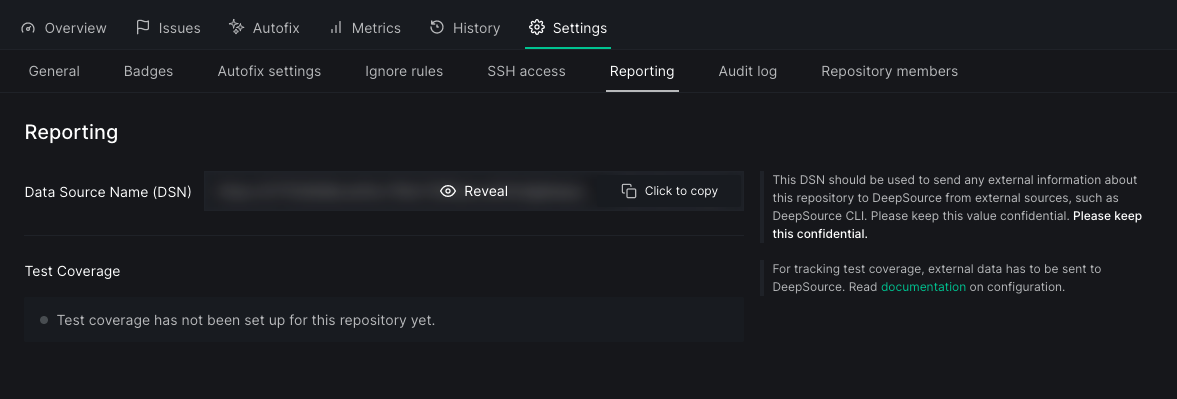
Once you get the DSN, store it as an environment variable named DEEPSOURCE_DSN in your CI's environment.
Installing DeepSource CLI in your CI enviroment
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
This command will create a bin directory in the command's current working directory, and deepsource CLI executable will be present inside bin. We will use this executable from now on.
Reporting coverage artifact using the cli
This is the final step. Once you have the Test coverage reports generated, you can send them to DeepSource using the CLI.
Here's what the command looks like:
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key <key> --value-file <absolute-path-of-the-coverage report>
In the above command, <key> is the language for which you'd be sending the coverage report.
Here's the whitelist of the keys and their respective formats we support.
| Key | Value format |
|---|---|
| python | XML (Cobertura), LCOV |
| go | cover.out (Generated) |
| javascript | XML (Cobertura), LCOV |
| ruby | JSON (SimpleCov) |
| java | XML (Jacoco/Clover), LCOV |
| scala | XML (Jacoco/Cobertura) |
| php | XML (Cobertura) |
| csharp | XML (Cobertura) |
| cxx | GCOV, LCOV |
| rust | GCOV, LCOV |
Please refer 'report' command of CLI documentation if you want to read more on the command usage.
Make sure you always run the above cli report command from the root of your repo. This will ensure that the file paths in your test reports are handled correctly, if present.
Failing to do that might result in issues not getting raised for your project. You'd still be able to see the metrics.
The maximum allowed size for the coverage report file is 20 MB.
Submitting Multiple coverage reports
DeepSource supports merging coverage reports implicitly. If you have multiple CI pipelines generating partial coverage reports, send them as soon as they are generated under the same key name. DeepSource will combine all of them to prepare a final result. For example, if two CI pipelines test platform-specific parts of a module, you can report both the artifacts and DeepSource will implicitly combine the results of the reports.
You'll notice a newly updated check every time you submit a new artifact. There's no time limit for sending multiple coverage reports.
The JaCoCo and Clover coverage formats report metrics for individual methods and may not contain data about the individual covered lines in the methods.
For such cases, DeepSource uses a max operation on the reported metrics to calculate the aggregate report. So if parts of certain methods are covered in different coverage reports, the reported line coverage for that method may be lower than the actual line coverage.
For example, if one report covers the top 25% lines for a method, and another report covers the bottom 25% lines for the same method, since there is no way of knowing if both the lines in the reports are different, DeepSource will report the coverage to be 25% even though it might be 50%. This is only a limitation for JaCoCo and Clover coverage formats at the moment.
Examples
JavaScript
Jest
Here are the steps to report JavaScript coverage data:
# Make sure `jest` is installed. If not, install it using `yarn`
yarn add --dev jest
# OR `npm`
npm install --save-dev jest
# Add the following options to the jest config to get a cobertura report
"collectCoverage": true,
"coverageReporters": ["cobertura"]
# Or, add these options as flags to test script in package.json
{
"scripts": {
"test": "jest --coverage=true --coverageReporters=cobertura"
}
}
# Run the tests
yarn test
# OR
npm test
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key javascript --value-file ./coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml
If the coverage file is generated at a path other than the root directory, pass that path to the value-file flag of deepsource report.
Example :
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key javascript --value-file ./src/app/coverage/cobertura-coverage.xml
Go
go test
The analyzer supports coverage profile (report) for all three modes — set, atomic, and count generated by the go test.
This is how you can generate a coverage profile and report it to the analyzer:
# Run your tests and generate coverage report
go test -coverprofile=cover.out
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out
Note: Tests for different Go packages
If you are running tests and generating coverage reports for different packages separately, you need to combine all generated coverage reports into a single file and submit that to the test-coverage analyzer.
This is how you can combine the coverage artifacts before reporting them:
# Run tests for a package
go test -coverprofile=cover.out ./somePackage
# Append coverage data in a separate file
cat cover.out >> coverage.out
# Run tests for another package
go test -coverprofile=cover.out ./someOtherPackage
# Combine the coverage data in the same way
cat cover.out >> coverage.out
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from the repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./coverage.out
Python
unittests
# Install coverage.py pacakage from pip
pip install coverage
# Run coverage
coverage run tests.py
# Generate coverage report in xml format
coverage xml
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
pytest
# Install pytest and pytest-cov pacakages from pip
pip install pytest pytest-cov
# Run pytest with --cov and --cov-report flags
pytest --cov=./ --cov-report xml
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
Reference: https://pypi.org/project/pytest-cov/
nose2
# Install nose2 package from pip
pip install nose2[coverage_plugin]>=0.6.5
# Run nose with --with-coverage and --coverage-report flags
nose2 --with-coverage --coverage-report xml
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
Reference: https://docs.nose2.io/en/latest/plugins/coverage.html
NOTE: Usage with tox
If you are using tox.readthedocs.io, make sure you omit .tox/* and env/* in your .coveragerc file because when running tests with tox, the coverage report will contain test report files other than your source (e.g., site-packages, etc.).
Here's an example of a .coveragerc file:
[run]
branch = True
source = src
omit =
.tox/*
env/*
With multiple python versions, combine the coverage data files before reporting.
Example tox.ini file:
[tox]
envlist = cov-init,py27,py36,py37,cov-report
skipsdist=True
skip_missing_interpreters=True
[testenv]
setenv =
COVERAGE_FILE = .coverage.{envname}
deps =
pytest
pytest-cov
coverage
commands =
pytest --cov
[testenv:cov-init]
skipsdist = True
setenv =
COVERAGE_FILE = .coverage
deps = coverage
commands =
coverage erase
[testenv:cov-report]
skipsdist = True
setenv =
COVERAGE_FILE = .coverage
deps = coverage
commands =
coverage combine
coverage report
coverage xml
Ruby
SimpleCov
First, install simplecov if it is not already installed.
gem install simplecov
Then, follow the steps below to generate a test coverage report.
- Add the following lines to the
spec_helper.rbfile inside thetestsfolder of your project:
# frozen_string_literal: true
require 'simplecov'
SimpleCov.start
- Add
--require spec_helper.rbto the.rspecfile. - Run rspec using
bundle exec rake rspecto generate a coverage report. - The coverage report will be available inside the
coveragefolder.
Once you have a coverage report, you can upload it to DeepSource using the following commands:
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value-file ./coverage/.resultset.json
SimpleCov writes coverage results to a .resultset.json file. This is what you will want to upload to DeepSource.
Java
The test coverage analyzer supports test coverage metrics for Jacoco and Clover XML reports.
Jacoco
Setting up test coverage differs with each type of build system (Maven, Gradle, etc.). Here's an example of the configuration needed to run Jacoco on a maven repo:
<!-- Within pom.xml -->
...
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<!-- attached to Maven test phase -->
<execution>
<id>report</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
...
Once you've added Jacoco to your project's pom.xml file, you should be able to run tests and generate the coverage report. The default location of the coverage report is target/site/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml. In case your project has multiple modules, you will need to use the jacoco:report-aggregate goal to merge all reports together.
mvn test
After you have the XML test report, you can upload it to DeepSource using the cli:
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set the DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from the reporting tab of
# your repository's DeepSource settings page.
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the project's root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file target/site/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml
You should be able to proceed similarly with other build systems, such as Ant or Gradle.
Reference: Jacoco documentation
Clover
DeepSource also supports reports generated using Atlassian's Clover coverage framework. Here's an example of using it with Maven:
...
<build>
<plugins>
...
<plugin>
<groupId>org.openclover</groupId>
<artifactId>clover-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>4.4.1</version>
<configuration>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>verify</phase>
<goals>
<goal>instrument</goal>
<goal>aggregate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.openclover</groupId>
<artifactId>clover-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>4.4.1</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</reporting>
...
Once you have added these elements to your project's pom.xml file, you will be able to instrument and run tests:
mvn clean clover:setup test clover:aggregate clover:clover
This will run tests and aggregate the results into a single clover report in the case of a multimodule project.
The default output directory for the report is target/site/clover/clover.xml.
After you have the XML test report, you can upload it to DeepSource using the cli:
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set the DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from the reporting tab of
# your repository's DeepSource settings page.
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the project's root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file target/site/clover/clover.xml
You should be able to proceed similarly with other build systems such as Ant or Gradle.
Reference: Clover documentation
Scala
Jacoco
Add sbt-jacoco to your project by adding the following line to your project/plugins.sbt -
addSbtPlugin("com.github.sbt" % "sbt-jacoco" % "<version>")
Then run sbt jacoco to generate the coverage report. You'll find the report in /target/scala-{version}/jacoco/report by default.
Note: To tweak Jacoco and its coverage behavior, you must change your build.sbt. See Jacoco's documentation for more information.
Once you have a coverage report, you can upload it to DeepSource using the following commands:
# Install deepsource CLI
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set the DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from the reporting tab of
# your repository's DeepSource settings page.
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the project's root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key scala --value-file target/scala-2.13/jacoco/report/jacoco.xml
Note: Since we support Cobertura for other languages as well, you should be able to follow similar steps as above for generating and uploading your Cobertura report.
PHP
PHPUnit
Currently, only the Cobertura XML format is supported by DeepSource.
Here are the steps to report PHP coverage data.
# Install phpunit/phpunit pacakage from composer
composer require --dev phpunit/phpunit
# Run coverage
vendor/bin/phpunit --coverage-cobertura coverage.xml
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key php --value-file ./coverage.xml
Rust
# Install cargo-llvm-cov from crates.io
cargo +stable install cargo-llvm-cov
# Run coverage against `cargo test`
cargo llvm-cov --lcov --output-path coverage.info
# or, to merge issues of multiple tests or runs
# cargo llvm-cov clean --workspace # remove artifacts that may affect the coverage results
# cargo llvm-cov run --no-report # run coverage
# cargo llvm-cov --no-report --features a # test coverage of feature `a`
# cargo llvm-cov --no-report --features b # test coverage of feature `b`
# cargo llvm-cov report --lcov # generate report without rerunning anything
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key rust --value-file ./coverage.info
C & C++
GCC & LCOV
# Install lcov using package manager
# Or, use https://github.com/linux-test-project/lcov/releases
# Before running your build tool add,
# -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage to the command line flags
# For CMake, add to the cmake project
# SET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-g -O0 -Wall -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage")
# SET(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "-g -O0 -Wall -W -fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage")
# SET(CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS "-fprofile-arcs -ftest-coverage")
# For makefile, add it to the default compile command
# From the directory with in which files .gcno and .gcda are located.
lcov –c –d . –o coverage.info
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key cxx --value-file ./coverage.info
C#
Via dotnet test
# Run your tests
dotnet test --collect:"XPlat Code Coverage" --logger:"console;verbosity=detailed" --results-directory /tmp/test-results/
# Install 'deepsource CLI'
curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh
# Set DEEPSOURCE_DSN env variable from repository settings page
export DEEPSOURCE_DSN=https://sampledsn@deepsource.io
# From the root directory, run the report coverage command and provide the absolute file path to the generated report.
# In this case, the filepath looks something like /tmp/test-results/abcf7e0-b7df-4b0c-b919-7cb480d0f123/coverage.cobertura.xml
#
# Make sure to double check the test run ID, i.e. the GUID and the file path.
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key csharp --value-file /tmp/test-results/<test_guid>/coverage.cobertura.xml
Reporting coverage from tests running in Docker container
Running tests inside a Docker container is a widely used practice in the software development community since it provides a consistent environment to run the application.
But, at the same time, it also adds isolation and, therefore, the test coverage reports generated inside the container are not accessible to the outside environment, i.e. the CI systems on which the testing pipeline is running.
However, the following two methods can be used to report the test coverage data to DeepSource.
Inside the Docker container
For reporting test coverage to DeepSource from inside the container which runs
tests, pass some environment variables to the container using the --env/-e flag.
docker run -e DEEPSOURCE_DSN -e GITHUB_ACTIONS -e GITHUB_REF -e GITHUB_SHA ...
docker run -e DEEPSOURCE_DSN -e USER -e TRAVIS_PULL_REQUEST_SHA ...
# Export the latest git commit hash as an environment variable
export GIT_COMMIT_SHA=$(git --no-pager rev-parse HEAD | tr -d '\n')
# Pass the exported environment variable to the container in which tests
# need to be run
docker run -e DEEPSOURCE_DSN -e GIT_COMMIT_SHA ...
Outside the Docker container
The test coverage report can also be reported by copying it from the Docker container in which tests are run to a shared directory which the host can also access.
# Creating a directory to store test coverage data in the host
# This directory will be mounted in the docker container as well
mkdir shared_coverage
# Run the Docker container which runs tests
# The `-v` flag sets up a bindmount volume that links the ~/coverage directory
# from inside the container to the ~/shared_coverage directory on the host machine.
docker run --name=test -v "~/shared_coverage:$HOME/coverage" ...
# Report the test coverage report stored in the shared directory to DeepSource
./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file
./shared_coverage/coverage.xml
In the Dockerfile of the container which runs test, make sure that the generated test coverage report is moved to the shared directory.
# In the container Dockerfile
mv coverage.xml ~/coverage
Tracking Coverage with CI
- How do I add Python Test Coverage to my CI/CD pipeline?
- How do I add Go Test Coverage to my CI/CD pipeline?
- How do I add Ruby Test Coverage to my CI/CD pipeline?
- How do I add Java Test Coverage to my CI/CD pipeline?
Add Python Test Coverage to CI/CD pipeline
Before proceeding further:
-
Go to the Settings page of the repository dashboard in DeepSource and copy the DSN from the Reporting section.
Do not add the
DEEPSOURCE_DSNvariable as part of any publicly visible configuration file. It contains sensitive information. -
Make sure that "Test Coverage" Analyzer is added to
.deepsource.toml. -
Ensure that you are running tests with
coverageorpytest-covfor pytest projects.
With Travis CI
-
On Travis CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add this to
.travis.yml:after_success: # Generate coverage report in xml format - coverage xml # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
With Circle CI
-
On Circle CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add the following step in
.circleci/config.yml:- run: name: Report results to DeepSource command: | # Generate coverage report in xml format coverage xml # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
With GitHub Actions
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository. Under your repository name, click "Settings". In the left sidebar, click Secrets.
- Type
DEEPSOURCE_DSNin the "Name" input box. - Add the value copied above.
- Type
-
When you checkout code, ensure that you use pull request HEAD commit instead of merge commit:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} -
Add the following step in
.github/workflows/main.yml:- name: Report results to DeepSource run: | # Generate coverage report in xml format coverage xml # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml env: DEEPSOURCE_DSN: ${{ secrets.DEEPSOURCE_DSN }}
With GitLab CI
-
Navigate to the project page of the repository on GitLab. Under project settings, in the sidebar, click on "CI/CD". Expand the variable section, and add the following:
- Type: "Variable"`
- Key:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - Value: The DSN value copied above
- State: Protected (Yes)
- Masked: No
- Scope: All Environments
-
Add the following under the test job in
.gitlab-ci.yml:test: script: # Install dependencies - pip install coverage pytest pytest-cov # Run tests - pytest --cov # Generate coverage report in XML format - coverage xml # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value file ./coverage.xml
With Heroku CI
-
Navigate to the app’s Settings tab in the Heroku Dashboard and then add the Config Variables:
- KEY:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - VALUE: The DSN value copied above
- KEY:
-
Run the following commands:
# Generate coverage report in xml format - coverage xml # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command for DeepSource to analyze it - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key python --value-file ./coverage.xml
Add Go Test Coverage to CI/CD pipeline
Before proceeding further:
-
Go to the Settings page of the repository dashboard in DeepSource and copy the DSN from the Reporting section.
Do not add the
DEEPSOURCE_DSNvariable as part of any publicly visible configuration file. It contains sensitive information. -
Make sure that the "Test Coverage" Analyzer is added to
.deepsource.toml.
With Travis CI
-
On Travis CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add this to
.travis.yml:after_success: # Generate test coverage report - go test -coverprofile=cover.out # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out
With Circle CI
-
On Circle CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add the following step in
.circleci/config.yml:- run: name: Report results to DeepSource command: | # Generate test coverage report go test -coverprofile=cover.out # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out
With GitHub Actions
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository. Under your repository name, click "Settings". In the left sidebar, click Secrets.
- Type
DEEPSOURCE_DSNin the "Name" input box. - Add the value copied above.
- Type
-
When you checkout code, ensure that you use pull request HEAD commit instead of merge commit:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} -
Add the following step in
.github/workflows/main.yml:- name: Report results to DeepSource run: | # Generate coverage report go test -coverprofile=cover.out # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out env: DEEPSOURCE_DSN: ${{ secrets.DEEPSOURCE_DSN }}
With GitLab CI
-
Navigate to the project page of the repository on GitLab. Under project settings, in the sidebar, click on "CI/CD". Expand the variable section, and add the following:
- Type: "Variable"`
- Key:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - Value: The DSN value copied above
- State: Protected (Yes)
- Masked: No
- Scope: All Environments
-
Add the following job in
.gitlab-ci.yml:deepsource: script: # Run tests and generate coverage report - go test -coverprofile=cover.out # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out
With Heroku CI
-
Navigate to the app’s Settings tab in the Heroku Dashboard and then add the Config Variables:
- KEY:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - VALUE: The DSN value copied above
- KEY:
-
Run the following commands:
# Run tests and generate coverage report - go test -coverprofile=cover.out # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command for DeepSource to analyze it - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key go --value-file ./cover.out
Add Ruby Test Coverage to CI/CD pipeline
Before proceeding further:
-
Go to the Settings page of the repository dashboard in DeepSource and copy the DSN from the Reporting section.
Do not add the
DEEPSOURCE_DSNvariable as part of any publicly visible configuration file. It contains sensitive information. -
Make sure that "Test Coverage" Analyzer is added to
.deepsource.toml. -
Ensure that you are running tests with
simplecov.
With Travis CI
-
On Travis CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add this to
.travis.yml:after_success: # Run tests and generate simplecov coverage - bundle exec rake rspec # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value-file coverage/.resultset.json
With Circle CI
-
On Circle CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add the following step in
.circleci/config.yml:- run: name: Report results to DeepSource command: | # Run tests and generate simplecov coverage bundle exec rake rspec # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value-file coverage/.resultset.json
With GitHub Actions
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository. Under your repository name, click "Settings". In the left sidebar, click Secrets.
- Type
DEEPSOURCE_DSNin the "Name" input box. - Add the value copied above.
- Type
-
When you checkout code, ensure that you use pull request HEAD commit instead of merge commit:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} -
Add the following step in
.github/workflows/main.yml:- name: Report results to DeepSource run: | # Run tests and generate simplecov coverage bundle exec rake rspec # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value-file coverage/.resultset.json env: DEEPSOURCE_DSN: ${{ secrets.DEEPSOURCE_DSN }}
With GitLab CI
-
Navigate to the project page of the repository on GitLab. Under project settings, in the sidebar, click on "CI/CD". Expand the variable section, and add the following:
- Type: "Variable"`
- Key:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - Value: The DSN value copied above
- State: Protected (Yes)
- Masked: No
- Scope: All Environments
-
Add the following under the test job in
.gitlab-ci.yml:test: script: # Install dependencies - bundle install # Run tests and generate simplecov coverage - bundle exec rake rspec # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value file coverage/.resultset.json
With Heroku CI
-
Navigate to the app’s Settings tab in the Heroku Dashboard and then add the Config Variables:
- KEY:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - VALUE: The DSN value copied above
- KEY:
-
Run the following commands:
# Run tests and generate simplecov coverage - bundle exec rake rspec # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command for DeepSource to analyze it - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key ruby --value-file coverage/.resultset.json
Add Java Test Coverage to CI/CD pipeline
Before proceeding further:
-
Go to the Settings page of the repository dashboard in DeepSource and copy the DSN from the Reporting section.
Do not add the
DEEPSOURCE_DSNvariable as part of any publicly visible configuration file. It contains sensitive information. -
Make sure that the "Test Coverage" Analyzer is added to
.deepsource.toml.
The examples given here use Jacoco with Gradle. The same steps apply to Clover/Maven apart from the commands used to generate the test coverage report.
With Travis CI
-
On Travis CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add this to
.travis.yml:after_success: # Generate test coverage report - ./gradlew test jacocoTestReport # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command # This example is with respect to Gradle. # The report directory will be different for Maven. - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file ./build/reports/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml
With Circle CI
-
On Circle CI, go to Settings > Environment Variables and add a
DEEPSOURCE_DSNenvironment variable with the DSN copied above as its value. -
Add the following step in
.circleci/config.yml:- run: name: Report results to DeepSource command: | # Generate test coverage report ./gradlew test jacocoTestReport # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file ./build/reports/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml
With GitHub Actions
-
On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository. Under your repository name, click "Settings". In the left sidebar, click Secrets.
- Type
DEEPSOURCE_DSNin the "Name" input box. - Add the value copied above.
- Type
-
When you checkout code, ensure that you use pull request HEAD commit instead of merge commit:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2 with: ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }} -
Add the following step in
.github/workflows/main.yml:- name: Report results to DeepSource run: | # Generate test coverage report ./gradlew test jacocoTestReport # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file ./build/reports/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml env: DEEPSOURCE_DSN: ${{ secrets.DEEPSOURCE_DSN }}
WIth GitLab CI
-
Navigate to the project page of the repository on GitLab. Under project settings, in the sidebar, click on "CI/CD". Expand the variable section, and add the following:
- Type: "Variable"`
- Key:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - Value: The DSN value copied above
- State: Protected (Yes)
- Masked: No
- Scope: All Environments
-
Add the following job in
.gitlab-ci.yml:deepsource: script: # Generate test coverage report ./gradlew test jacocoTestReport # Install deepsource CLI curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file ./build/reports/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml
With Heroku CI
-
Navigate to the app’s Settings tab in the Heroku Dashboard and then add the Config Variables:
- KEY:
DEEPSOURCE_DSN - VALUE: The DSN value copied above
- KEY:
-
Run the following commands:
# Generate test coverage report - ./gradlew test jacocoTestReport # Install deepsource CLI - curl https://deepsource.io/cli | sh # From the root directory, run the report coverage command for DeepSource to analyze it - ./bin/deepsource report --analyzer test-coverage --key java --value-file ./build/reports/jacoco/jacocoTestReport.xml